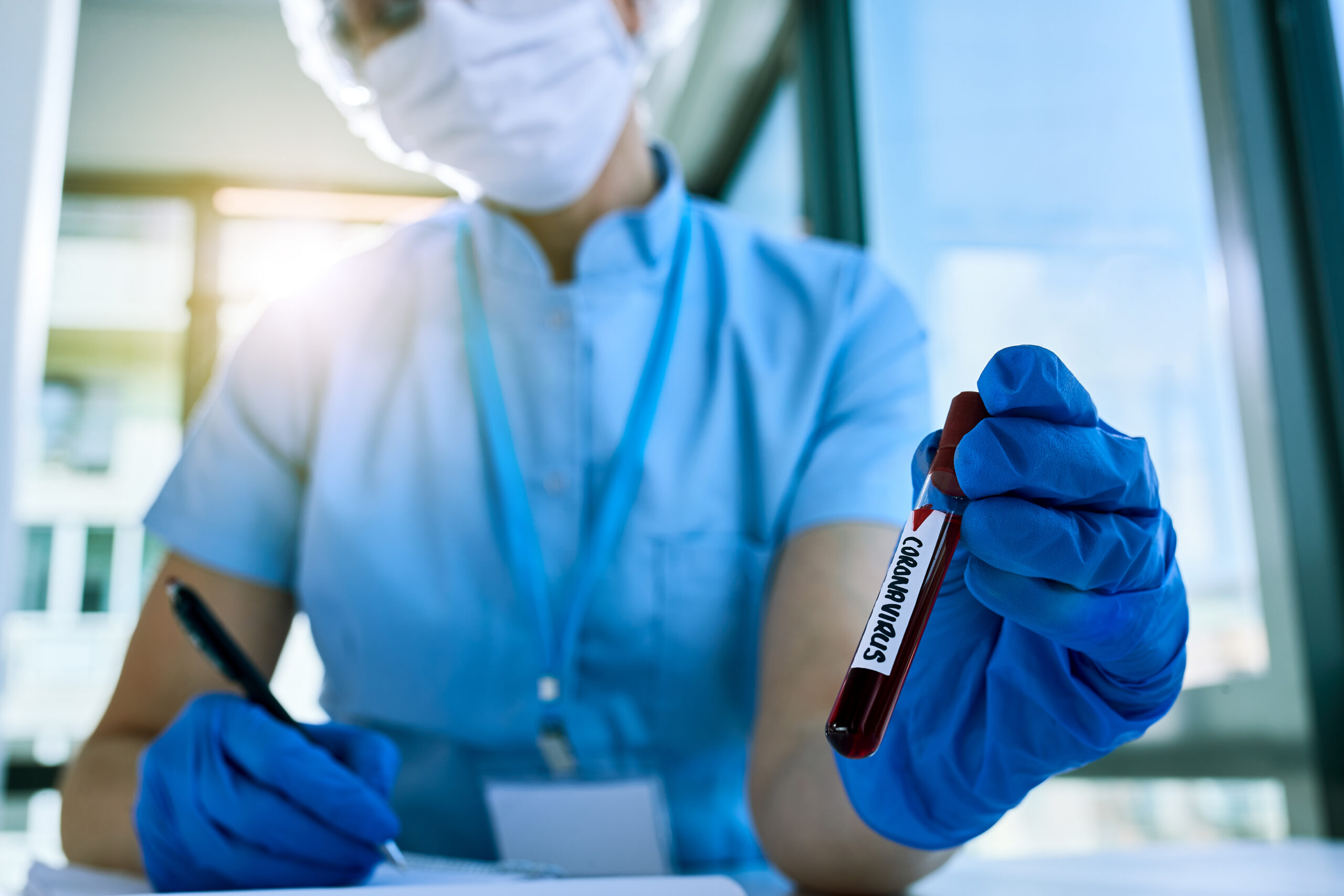
In the world of trauma care, the timely administration of blood transfusions can mean the difference between life and death. As the ambulance services evolve, healthcare professionals are increasingly recognizing the critical importance of prehospital blood transfusion protocols. This innovative approach not only aims to reduce mortality rates but also enhances the overall effectiveness of trauma response strategies. In this article, we will explore the current advancements in prehospital blood transfusion, the challenges faced in its implementation, and actionable insights for trauma care providers.
Understanding Prehospital Blood Transfusion
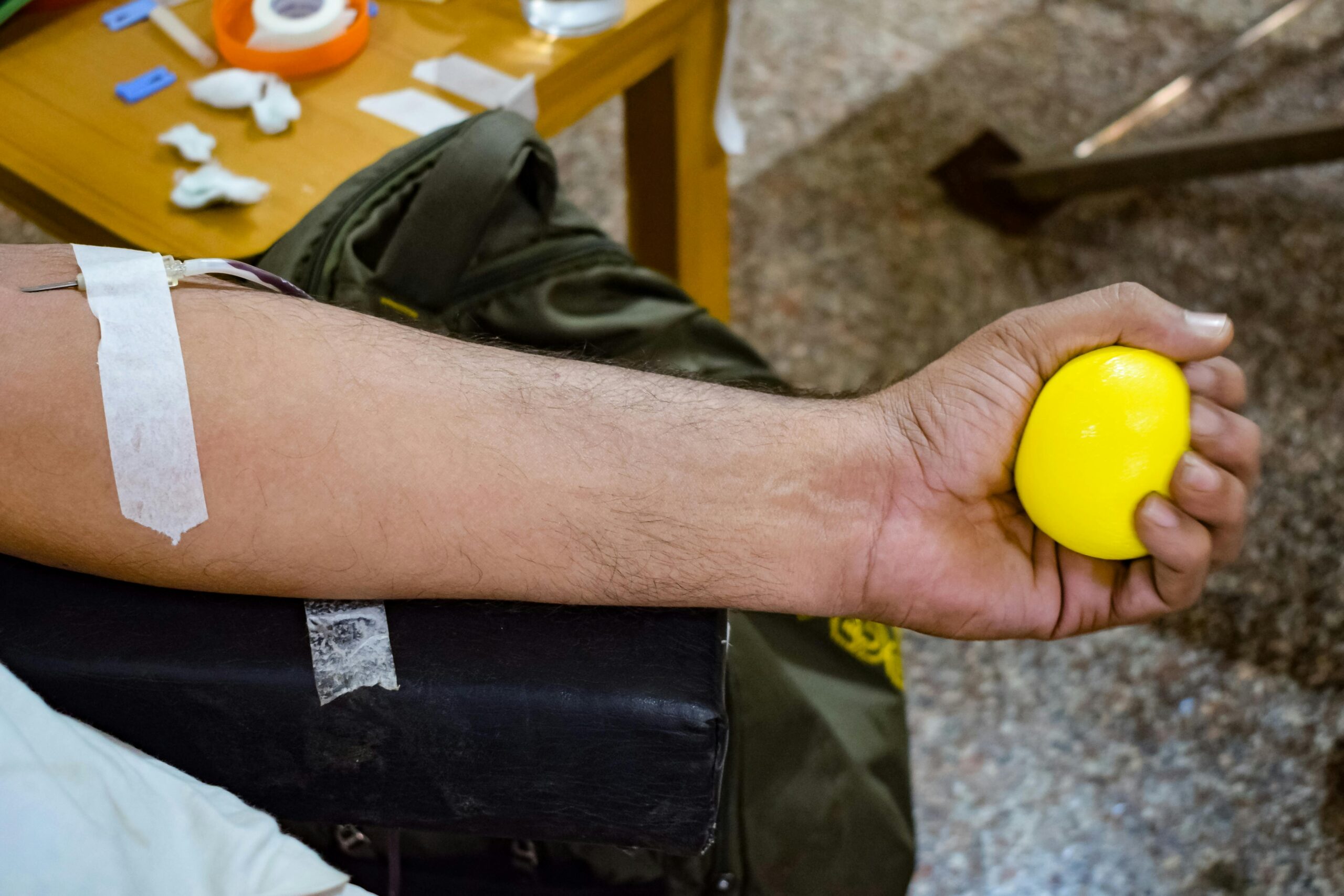
Prehospital blood transfusion refers to the delivery of blood products to patients before they arrive at a hospital. Typically administered by paramedics or emergency medical technicians (EMTs), this procedure has shown promising results in improving patient outcomes, particularly for trauma patients with significant blood loss. Because seconds can be critical in emergency situations, integrating effective transfusion protocols into prehospital care is essential.
Key Advantages of Prehospital Blood Transfusion
- Reduces Mortality Rates: Studies indicate that early administration of blood products can significantly lower mortality rates among trauma patients. For instance, research shows a 30% reduction in mortality when transfusions occur prehospital.
- Enhances Patient Stabilization: By providing essential blood components, prehospital transfusions can stabilize patients, allowing for better management of symptoms during transport.
- Improves Trauma Care Protocols: The integration of transfusion protocols in ambulance services streamlines treatment procedures, leading to quicker and more efficient responses.
Key Challenges in Implementing Prehospital Transfusion
While the benefits of prehospital blood transfusion are clear, several challenges hinder its widespread adoption.
- Training and Competency: One primary challenge is ensuring that emergency responders are adequately trained in transfusion procedures. Effective training programs can enhance teams’ confidence in administering blood products, as results show that familiarization with procedures improves the speed and efficacy of administration.
- Logistical Concerns: Maintaining blood product viability during transport poses logistical hurdles. Ambulance services must establish robust systems for blood storage and monitoring to ensure quality before administration.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the regulatory landscape surrounding blood transfusion can be complex. Emergency services must ensure compliance with existing laws and guidelines to mitigate legal risks.
Recent Advancements in Prehospital Transfusion Protocols
Significant improvements in technology and protocols for prehospital blood transfusion have emerged in recent years. The availability of blood products in hospitals and blood banks has increased, thanks in part to better inventory management systems. Moreover, point-of-care testing tools enable rapid assessment of a patient’s blood type and condition, ensuring appropriate and timely transfusions.
For example, portable blood warmers allow healthcare providers to safely warm blood products before administration, improving patient comfort and increasing the likelihood of a successful transfusion. The introduction of pre-packaged blood products that do not require cross-matching has also simplified the process, thereby expediting treatment.
Actionable Insights for Trauma Care Providers
As healthcare professionals in the ambulance services sector, it is crucial to stay abreast of advancements in prehospital blood transfusion. Here are some actionable insights to enhance your trauma care capabilities:
- Invest in Comprehensive Training: Regularly schedule training sessions focused on transfusion protocols. Include simulations that replicate real-life scenarios to boost confidence and proficiency among your emergency response teams.
- Develop Robust Protocols: Establish clear protocols regarding when and how to administer prehospital transfusions. Create an easy-to-follow checklist that guides personnel through the process, ensuring consistency and reliability.
- Leverage Technology: Adopt technological solutions, such as blood warming devices and rapid testing kits, to optimize the transfusion process. Regularly evaluate new products and innovations that can further enhance patient outcomes.
Future Trends in Prehospital Blood Transfusion
Looking ahead, the future of prehospital blood transfusion appears promising. Innovations in telemedicine could facilitate real-time consultations between paramedics and hospital trauma teams, ensuring that care decisions are made collaboratively based on the latest patient information. Additionally, as outcomes from prehospital transfusions are closely monitored, data collected may inform future best practices and guidelines, continually refining the approach to trauma care.
Furthermore, community education on trauma awareness and injury prevention can bolster early intervention approaches, equipping citizens with knowledge that could save lives before ambulances even arrive.
Conclusion
Prehospital blood transfusion is a critical aspect of modern trauma care, providing timely interventions that significantly reduce mortality and improve outcomes for trauma patients. While challenges remain, such as training and logistical hurdles, embracing the advancements in this field can empower healthcare professionals to deliver exceptional care.
As the ambulance services sector continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest protocols and advancements in blood transfusion is essential. By investing in training, leveraging technology, and developing robust protocols, trauma care providers can ensure they are well-equipped to save lives in critical moments.
For more information on how to integrate effective prehospital transfusion protocols into your practice, learn more about integrating prehospital transfusion protocols. Collaboratively, we can enhance the efficiency of trauma care and ultimately improve patient survival rates in emergencies.
“`